線上影音
Home > ANSYS HFSS 教學 > Stripline Differential Pair
本文始於2009年筆者初入SI、PI領域時,使用Ansoft HFSS v10.0完成操作,模擬步驟與說明較為簡略,也沒有附上範例檔。2012年重新以HFSS v14.0撰寫本文,並附上範例檔供學習參考。此例的重點在了解Driven Terminal下wave port + de-embed使用,與differential pair的odd mode、even mode field,並做特性阻抗最佳化求解。
-
問題與討論
11.2 在HFSS中,如何觀察Zin(從port往系統網路看)、埠端阻抗(port Zo)與傳輸線特性阻抗(Zo)?
11.3 為何此例在HFSS內模擬時,不需要設background (air box)? 又此例stripline的reference plane在哪裡?
11.4 什麼時候用wave port,甚麼時候用lump port?此例如果改成lump port,結果會不會相同?
11.5 如果step3.3不用de-embed,而是真正建一段線長1000mils的傳輸線取代本例100mils線長+900mils de-embed,結果相同嗎?
![]()
1.1 Setting Tool Options
Tools \ Options \ HFSS Options: 被複製的幾何形物件,默認有一樣的邊界特性
Tools \ Options \ Modeler Options:
1.2 Open a new project:File \ New
如果希望一開啟HFSS就已經有一個new project,請從Tools \ Options \ General Options:
1.3 Set Solution Type:HFSS \ Solution Type, choose [Driven Terminal] for this example
讀者可以用Help搜尋[Solution Type]的說明:
[Driven Mode] is for calculating the mode-based S-parameters of passive, high-frequency structures such as microstrips, waveguides, and transmission lines which are "driven" by a source, and for computing incident plane wave scattering. The S-matrix solution will be expressed in terms of the incident and reflected powers of waveguide modes.
[Driven Terminal] is for calculating the terminal-based S-parameters of passive, high-frequency structures with multi-conductor transmission line ports. This solution type results in a terminal-based description in terms of voltages and currents.
[Eigen Mode] is for calculating the Eigenmodes, or resonances, of a structure. The Eigenmode solver finds the resonant frequencies of the structure and the fields at those resonant frequencies. Eigenmode designs cannot contain design parameters that depend on frequency.
[Transient] is for calculating problems in the time domain. It employs a time-domain "transient" solver. Typically applications include (The mode appears from HFSS 13)
1.4 Set Model Units:Modeler \ Units, select "mil"
小心不要選錯成[mile],差一字可是差很多的
1.5 Set Default Material:直接從工具列選擇
在"Search by Name"欄位內填入"pec" (means perfect conductor),下面視窗內即會自動搜尋到該名稱的材質,然後按"確定"即可。這個設定步驟,是確保我們等等畫的signal trace材質是良導體(默認pec)。
雖然本例使用的材質介電係數是不隨頻率變化,但HFSS可設定隨頻率變化的介電係數,請參閱
目標是模擬線寬W=6mils、線距S=18mils、線長1000mils的differential pair,堆疊結構則是線銅厚0.7mils,訊號線夾在高度26mils的substrate中,介電係數4.4,沒有另外再畫其他的金屬平面 。
2.1 Create trace 1, trace 2
2.1.1 畫傳輸線實體結構有兩種方法,HFSS v12以前的文件是用Drow \ Box,HFSS v13以後的文件是用Draw\Line + CreatePolyline。後者在畫傳輸線的應用上,會方便許多。
- Draw \ Box
按下後,下方狀態列會出現座標輸入欄位 ,請輸入對角兩點的座標(基準座標與相對座標)
接著會彈出物件屬性編輯窗,將原本"position"該列中的9mil改寫成S/2,接著在跳出的變數定義窗中定義S=18mil;同理定義W=6mil。然後選擇"Attribute"標籤頁,更改Name type=trace1
- Draw \ Line
from (0, 0, 0) to (100, 0, 0), and rename in [Attribute] tab as "trace1"
Edit \ Select All
Edit \ Arrange \ Move from (0, 0, 0) to (0, 9, 0), and a Properties window will launch
2.1.2 上述步驟完成後,可以從View \ Fit All \ Active View或按Ctrl+D 檢視全貌
2.1.3 先在History Tree內由Object \ pec \ trace1選定上一步驟所繪製的trace1,按滑鼠右鍵選擇"Mirror"
以上步驟,也可以由Edit \ Select All Visible + Edit \Duplicate \ Mirror完成。
此時游標變成一個較大的黑色實心菱形,以指定鏡射方向;當然也可以透過輸入基準座標與相對座標來指定鏡射方向。(往-Y軸方向翻)
接著會彈出物件屬性編輯窗,選擇"Attribute"標籤頁,更改Name type=trace2
2.2 Create Substrate of permittivity =4.4
直接從工具列選擇
,按"Add Material",新建一個電介係數為4.4的材質,命名為My_FR4
畫包圍傳輸線的substrate (dielectric)實體結構同樣有兩種方法
Draw \ Box按下後,請輸入基準座標與相對座標(0,-100,-13)(100,200,26),然後在屬性設定窗中,在"Attribute"標籤頁內,將名稱改成substrate,透明度Transparency改成0.8
- Draw \ Line from (0, 0, 0) to (100, 0, 0),然後其Properties內的Type選[Rectangle],Width/Diameter=200,High=26,透明度設0.
3.1 Create wave port excitation p1, p2
3.1.1 Edit \ Select \ Faces
Edit \ Select \ By Name
3.1.2 HFSS \ Excitations \ Assign \ Wave Port
將此wave port命名為p1, 然後按OK。
導體延伸到air box,wave port直接下在air box的面上,這是典型的external wave port;另有一種internal wave port的做法,需要在wave port的另一邊貼一個導體平面。
同理在對面的face也建wave port。
3.2 Set Differential Pairs
HFSS \ Excitations \ Differential Pairs 或到Project window內的Excitation點右鍵選擇[Differential Pairs]
連續按兩次[New Pair]
3.3 Set de-embed distance of the transmission line
HFSS \ List 選擇[Excitation] tab,也可以看到p1, p2
選擇p2,然後按"Properties",[Deembed]打勾,[Deembed Distance]填-900mil
[Deembed]這是HFSS在模擬傳輸線時,一個很好用的功能;user只需建一小段的固定傳輸線模型,然後設定De-embed Distance,即可任意調整傳輸線長度,不需rerun而得到模擬結果。以此例來說,我們想要模擬1000mils長的傳輸線,但我們所建的模型只有100mils,所以設定De-embed Distance=-900mils(即延長傳輸線長度900mils)。設定後可以看到一根粗的藍色線,標示傳輸線長度的延伸。
3.4 Verify the boundary:HFSS \ Boundary Display (Solver View)
背景環境有默認的boundary
本例不需要另外框一個背景輻射空間,原因是因為訊號線已經被包在一個已經有設定屬性的材質裡了(substrate, My_FR4),且因為wave port正好佈滿兩側,wave port的四邊所延伸的四面,其邊界條件默認是Perfect Conductor。
-
4.1 HFSS \ Analysis Setup \ Add Solution Setup
或是按滑鼠右鍵
[Solution Frequency]若取整個系統設計的最大考慮頻寬,mesh會切最多,模擬時間較長,但模擬也會最準。
對於天線設計,因為我們通常只在意天線操作頻帶,所以這個值可以設天線阻抗最低的操作頻點;但對於SI設計的應用,則建議取0.5/Tr值。
[Maximum Number of Passes] is the maximum number of mesh refinement cycles for HFSS to perform. 設大於2(含)就會mesh refinement,設的越大,可容許的refine tuning次數越多,模擬時消耗的記憶體也越多(一般設10~20), 但若mesh refinement提前達到[Maximum Delta S]條件就會停下來
[Minimum Converged Passes]設定建議從1改成2,mesh refinement的次數會多一次,但可以確保meshing切的真正足夠
Zero order、First order(default)、Second order,會分別自動對應"Lambda Refinement"為Target 0.1、0.3333、0.6667,越高階order越適合用來解結構複雜的模型,但時間也會花較多。HFSS v12以後多了[Mixed Order],建議默認用此 檔設定,會在結構較複雜或電場變化較大的地方,自動以high order處理
[Enable Iterative Solver]:The iterative solver significantly reduces memory usage, and it can also provide a savings in the solution time for large simulations.
4.2 HFSS \ Analysis Setup \ Add Frequency Sweep
或是按滑鼠右鍵
[DC Extrapolation]只有當[Sweep Type]選擇[Interpolating]才 有,且Start Frequency設0時,[DC Extrapolation]的最小頻率才能指定
[Sweep Type] 選[Discrete]就是針對指定的頻點老實求解,費時較久但較準確, 一般5GHz內的頻寬適用。[Fast]適用於 局部窄頻段內頻率響應變化大的題目,如特性振盪的頻段(resonant frequency),可以在指定求解的頻點小範圍內精準。[Interpolating]則適用於寬頻帶(10GHz~)且頻率響應較緩和的(smooth)題目。
4.3 HFSS \ Validation Check
HFSS \ Analyze All
-
5.1 HFSS \ Results \ Solution Data
查看模擬過程中花多少時間,用了多少記憶體資源
查看模擬過程中做了幾次疊代才得到收斂值
總共切多少mesh
每次跑的結果不一定相同,若電腦太遜,還有可能跑一跑就Error而跑不出結果。這些訊息可以在執行過程中real time check。
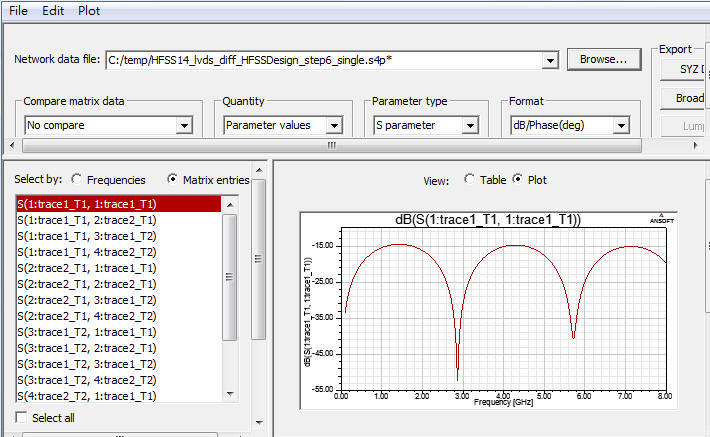
5.2 S-parameter plot
HFSS \ Results \ Create Terminal Solution Data Report \ Rectangular Plot
5.3 從SDD11可以看出此1000mils的傳輸線,在2.92GHz、5.84GHz有共振點
HFSS \ Results \ Solution Data,[Display All Freqs]打勾,按[Export Matrix Data]即可另存.snp file (.snp)
若按[Equivalent Circuit Export],則可輸出PSpice.lib或HSPICE.sp
6.1 Set the field excitation:HFSS \ Fields \ Edit Sources,設定p1 drive,p2 terminated
或是按滑鼠右鍵
6.2 Create a field plot:HFSS \ Fields \ Fields \ E \ Mag_E (能量大小顯示)
HFSS \ Fields \ Modify Plot Attributes
或是
若從[Edit Source]修改[Phase]設定,可以看出Mag_E場圖的變化 ,下圖左是common mode,圖右是differential mode
6.3 Create a field plot:HFSS \ Fields \ Plot Fields \ E \ Vector_E (方向顯示)
HFSS \ Fields \ Modify Plot Attributes
在6.5<W<7.5mils,16.5<S<17.5mils求解最佳化設計
7.1 Add a parametric sweep:HFSS \ Optimetrics Analysis \ Add Parametric
7.2 Run Analysis
7.3 HFSS \ Results \ Create Terminal Solution Data Report \ Rectangular Plot
隨著線距S的增加,差分特性阻抗變大;同樣線距下,W越小特性阻抗越大。
step 7.1~7.3還不算是真的用HFSS做最佳化設計,真的最佳化求解的做法如下
7.4 Add Optimization
[HFSS] \ [Design Properties]
[HFSS] \ [Optimetrics Analysis] \ [Add Optimization]
7.5 Run Optimize Analysis
此例如果採用[Pattern Search]做最佳化,3次收斂
此例如果進採用[Quasi Newton]做最佳化,11次收斂
透過查詢on line help [Choosing an Optimizer]可知,對於少變數(2D~3D search)的簡單題目,用[Pattern Search]比用[Quasi Newton]好。但不管是[Pattern Search]或[Quasi Newton],在做最佳化搜尋時,預設給的搜尋範圍與初始計算值,會影響最佳化搜尋的效率。
8.1 Double click on Mag_E
8.2 Mag_E \ Animate
8.3 Setup Animation:可以分別選擇"Swept Variable"為Phase、S、W,按OK
Follow step5.4
HFSS可以支持吐出single-end S-parameter as step5.4,或是differential S-parameter as step9。但如果我們並沒有3D model,只有S-parameter (.snp),那如何在single-end與differential間做轉換呢?
Designer 6.0有提供一個非常好用的功能:Tool \ Net Data Explorer,不但可以把single-end轉differential S-parameter,還可以把S參數轉Z參數
Edit \ Define Differential Pairs
11.1 De-embed有什麼優點?
Ans:讀者可以把本文step3.3中的[Deembed Distance]值,改填-900mm(不需rerun),即可看到S plot結果如下,諧振頻點從低頻到高頻(變多 變密),S11也從-15dB下降到-24dB。透過這方式,user不需重新建模,可以快速調整結構長度,而且不需重新mesh或模擬計算。如果不用這方式,而是把3D model的長度參數設變數,那越長的結構模擬時間會增加越多。
11.2 在HFSS中,如何觀察Zin(從port往系統網路看)、埠端阻抗(port Zo)與傳輸線特性阻抗(Zo)?
Ans:在step5.2中,Category:Terminal Port Zo即是指port端阻抗,而不是傳輸線上的特性阻抗,不要搞錯了。Category:Terminal Z Parameter即是指從port往系統網路看的阻抗Z11 。而傳輸線的特性阻抗若要在HFSS查看,則要到時域裡看TDR。
11.3 為何此例在HFSS模擬時,不需要設background (air box)? 又此例stripline的reference plane在哪裡?
Ans:默認的background boundary (substrate表面)是理想導體,若不考慮reference plane的導電率,傳輸線就直接以boundary face當reference plane。為了驗證這點,我們在上下表面各貼一層Perfect E的sheet當reference plane,重新下wave port,且該wave port同時以此上下兩sheet為reference,模擬結果如下,與step5.3一模一樣
11.4 什麼時候用wave port,甚麼時候用lump port?此例如果改成lump port,結果會不會相同?
Ans:wave port是以平面能量來計算,lump port是以V/I來計算,如果lump port夠短,可以得到很接近的S-parameter模擬結果 ,除非wave port size設的不對。 一般天線或波導管設計建議用wave port,SI設計建議用lump port,但沒有絕對。Lump port也可設de-embed,也可以設成參考上下兩平面,但lump port與wave port的de-embedded是不同的。前者是K掉lump port的電感效應port calibration(所以我們建議lump port越短越好),後者是以後處理的方式影響S參數結果,試算不同的傳輸線長度。
11.5 如果step3.3不用de-embed,而是真正建一段線長1000mils的傳輸線取代本例100mils線長+900mils de-embed,結果相同嗎?
Ans:與step5.3的模擬結果相比, 在3GHz S11大約差4dB,諧振頻點約偏移3%,在6GHz S11大約差12dB。故太長的wave port de-embed是會造成S11誤差的 ,雖然這誤差很小,建議de-embed長度最好不要超過l/10
12.1 SI issue for high speed serial differential interconnection -- 中華大學 薛光華老師
12.2 EMC Considerations for Differential Lines , 2007
12.3 Differential Signals are NOT Immune to EMI/EMC Concerns! , 2010
12.4 HFSS v13,v12與v11的差異? -- ANSYS